TCP/IP is a network protocol. It defines the language (rules) that your computer uses to communicate with other computers on the network. While most network devices on the local area network are configured as DHCP clients, you can also manually modify the TCP/IP configuration for any host on the network.
If you do use DHCP on your network, you do not have to change your settings if you move your IP hosts from one location to another. With DHCP, you also do not have to worry about configuring any additional settings on the client such as DNS or WINS. However, as previously mentioned, you may need to change the configuration of a DHCP client to one that uses static IP settings.
Depending on the version of Windows Operating System, you can access the TCP/IP settings by either accessing the Network and Sharing Center (Vista/2008 and later) or right click the desired connection from the Network Connections folder (XP/2003 and earlier).
Choose properties to open the Properties dialog of the selected connection. Next, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) from the list and click the Properties button. For XP/2003 and earlier, you will just see TCP/IP as an option. For Vista/2008 and later, you will see IPv4 and IPv6 listed.
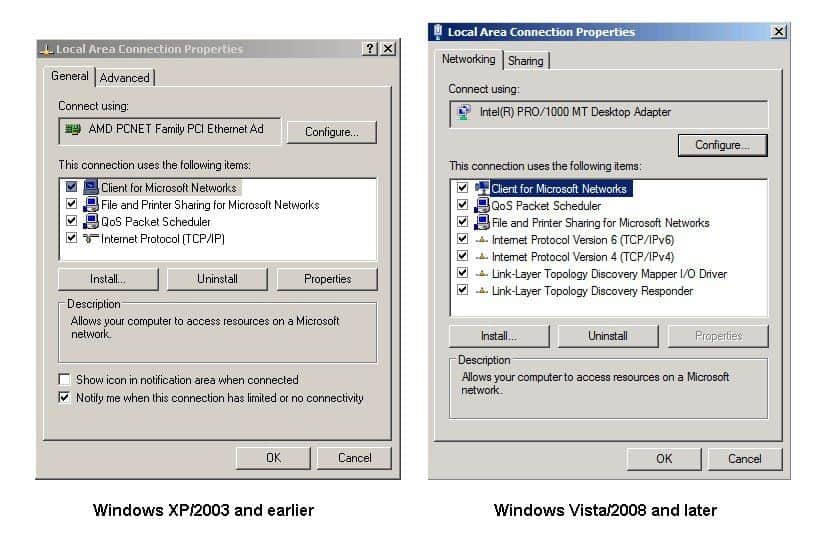
In the video tutorial associated with this tutorial, the various properties for IPv4 are discussed. Some of the options covered in the tutorial are DHCP versus Static configuration, and advanced DNS and WINS options as well.