In the Active Directory (AD) Forest model, a service is needed to provide information about objects that live in the forest. That is where the Global Catalog server comes into play. The global catalog is a partial, read-only replica of all other domain partitions in the forest. In other words, the global catalog server will contain limited information that is stored in the various domains in the forest.
The attributes that are included in the global catalog are those that are most used for searching. The global catalog can be used to find objects in the forest regardless of how many domains are members of the forest. Searches that are used on Global Catalog servers are fast and efficient because the data is stored in the local database on the server.
There is no need to refer the requestor to a domain controller in another domain. The global catalog is stored on domain controllers that have been assigned this role. The global catalog data is replicated through normal multi-master AD replication.
The information in the Active Directory schema determines which attributes are marked as global catalog data. The attribute called isMemberOfPartialAttributeSet determines if the attribute will be a part of the global catalog data. If the attribute is set to true, it is included.
Fortunately, schema administrators can add additional attributes to be included in the global catalog if they see a need to do so because the attribute(s) is routinely searched. For example, the attribute, Division, is not included in the global catalog by default.
However, if this attribute is routinely searched, it may be beneficial to include it in the global catalog. To add an attribute to the global catalog, log in the domain as a Schema Administrator, launch a Microsoft Management Console (MMC), add the Schema snap-in. Before you have access to the Schema snap-in you must register the dll by opening the run command and typing regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll.
Once you open the Schema Admin snap-in, expand Attributes, and locate the attribute that you want to modify. Select Replicate this attribute to the Global Catalog option.
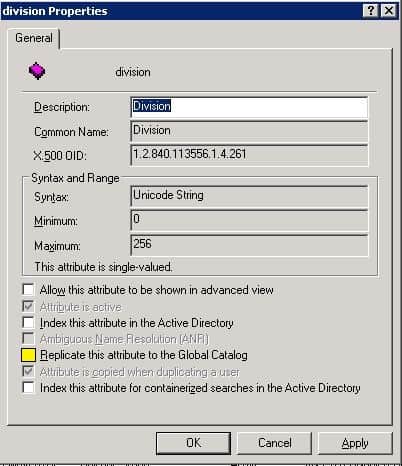
Use caution when adding additional attributes to the global catalog. This will cause the global catalog to replicate this information to other global catalog servers so you should expect an increase in network traffic and server resources, at least during the replication cycle.
In addition to the faster-searching capabilities, the Global Catalog Server is also used when processing user logons. Every time a user logs on to the domain, a Global Catalog Server is contacted. The reason is that the user’s membership in Universal Groups must be validated before a user can log on to the domain.
Universal Groups by nature can contain user and group accounts from any domain in the forest. In order to create an accurate security token, the global catalog must be checked to determine the universal group membership for the user.
Lastly, Global Catalog Servers are used to process logons when users use a User Principal Name (UPN) to log on. UPNs can be used to log on to computers in any domain in the forest.
The UPN format is email protected since the Global Catalog server is so important in the login process, it is recommended that each domain contain at least two Global Catalog Servers. By default, the first domain controller in the forest is assigned this role.











